Higgstec T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH Touch Screen Panel
- Model
- T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH
Item specifics
- Warranty
- 365 Days
- Shipping
- DHL/FedEx/UPS/TNT/EMS/Aramex /DPEX
- Touch points
- Single-touch
- Place of Origin
- China
- HMI touch glass
- touch digitizer glass
- HMI panel glass
- touch screen monitor
- Name
- T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH Touch Screen Panel
Review
Description
Higgstec T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH Touch Screen Panel

T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH touch screen
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH touch panel
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH Touch screen glass
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH Touch screen hmi
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH touch memrbane
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH touch digitizer
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH touchscreen
T171S-5RA001X-0A28R0-300FH HMI touch glass
5-Wire Resistive Touch Solution
Extremely stable, reliable and immune to electromagnetic interference, resistive touch technology remains popular today for critical applications such as for medical, aerospace and military use. Higgstec specializes in production of 5-Wire Resistive technology because of its superior endurance and reliability. 5-wire resistive screens don't require repeated calibration and can continue to function even when the surface has been scratched or damaged, because both the X and Y axis are detected on the lower (glass) layer, while the upper (film) layer is used as loop conduction only
Higgstec also uses a special high temperature production process for its resistive screens to fuse the silver sensor circuit onto the glass, preventing it from peeling off during extreme temperature or humidity variations, ensuring greater longevity and durability in harsh operating environments
A front cover shield (glass, fiberglass, PMMA or other material) can also be added to the front of the resistive panel for anti-abrasion and chemical resistance protection.


FAQ:
Question: Inspection Methods:
Answer:
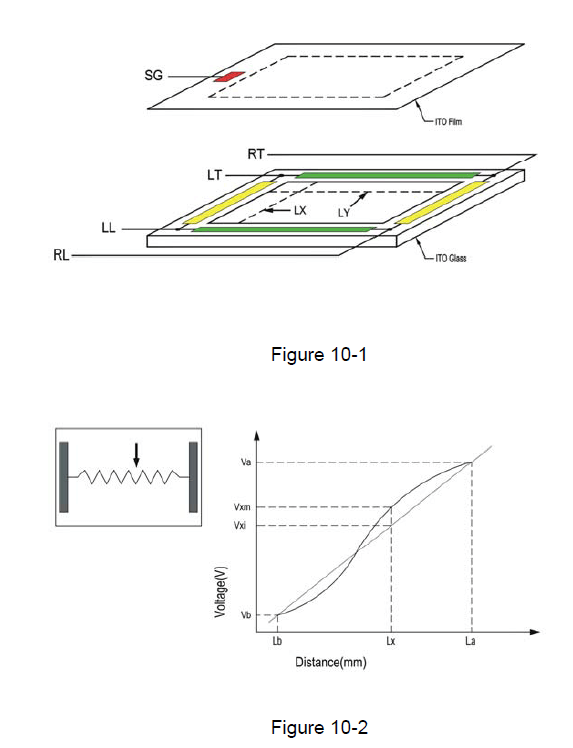
Linearity Condition
Step 1: short RT and RL(or short RL and LL).
Step 2: apply voltage DC 5V.
Step 3: short LT and LL (or short RT and LT).
Step 4: apply grounding.
Step 5: draw points along LX and LY at 5.0mm intervals within
pattern area and detect the voltage at SG.
Step 6: measure the voltage differences between RT and LT
(or RT and RL) (Fig 10-1) (Fig 10-2)